- What is a backconnect proxy?
- Are backconnect rotating proxies any different?
- Rotating backconnect proxies' use cases
- Backconnect proxies' pros and cons
- Analyzing how they work
- Understanding rotation and pools
- Choosing the right tool for the job
- Additional benefits that backconnect proxies offer
- Frequently Asked Questions


The world of networking has a myriad of proxy types, all of which can be categorized in various ways:
- Device type: mobile / desktop proxies.
- General focus: datacenter / residential proxies.
- Rotation: proxies that support rotation — and those that don’t.
To better capitalize on the given proxy type, you need to understand how it works — and if it has any alternatives. In this article, we’re going to look at backconnect proxies: namely, how they function and how they compare to classic (i.e. unmanaged) proxies.
We felt that this topic would benefit from a visual explanation, so we made a video on the backconnect rotating proxy:
Alternatively, you can read the text version below.
What is a backconnect proxy?
Backconnect proxies are a type of proxy server that provide users with a high level of anonymity and flexibility. Unlike regular proxies, which require users to manually configure and rotate their IP addresses, backconnect proxies automatically assign a different IP address from a large pool of proxies for each request. This way, users can avoid being blocked or detected by websites that monitor IP activity.
Backconnect proxies work by connecting users to a gateway server, which acts as an intermediary between the user and the target website. The gateway server then selects an IP address from a pool of available proxies, based on the user’s preferences and needs. The pool of proxies can consist of residential, datacenter, or mobile IPs, depending on the provider. The user does not need to know or manage the IP addresses behind the gateway server, as they are shuffled and rotated regularly.
Are backconnect rotating proxies any different?
Backconnect rotating proxies are the same as backconnect proxies, as they both rotate the IP address after every request or a certain period of time. The term "rotating" is sometimes added to emphasize the dynamic nature of these proxies, as opposed to static proxies that keep the same IP address for a longer duration. However, both terms refer to the same type of proxy server that provides users with a high level of anonymity and flexibility.
Rotating backconnect proxies' use cases
Backconnect proxies have many use cases, especially for large-scale web scraping and data extraction projects. Some of the common use cases are:
Web scraping: Backconnect proxies allow users to scrape data from multiple websites without being blocked or detected by anti-bot tools. Users can customize their proxy parameters, such as location, rotation time, session duration, and more, to optimize their scraping performance and accuracy.
Market research: Backconnect proxies enable users to collect and analyze data from various sources, such as competitors, customers, suppliers, and trends. Users can access geo-restricted or localized content by using proxies from different countries or regions.
SEO monitoring: Backconnect rotating proxy helps users to monitor and improve their search engine optimization (SEO) strategies. Users can track their rankings, keywords, backlinks, and traffic from different search engines and locations.
Ad verification: Backconnect proxies assist users to verify and protect their online advertising campaigns. Users can check if their ads are displayed correctly and effectively on different websites and platforms. Users can also detect and prevent ad fraud, such as click fraud, impression fraud, and domain spoofing.
Social media management: Backconnect proxies support users to manage multiple social media accounts and profiles. Users can create and post content, interact with followers, monitor feedback, and analyze metrics from different social networks and locations.
Backconnect proxies' pros and cons
Backconnect proxies have many advantages over regular proxies, especially for large-scale web scraping and data extraction projects. Some of the benefits include:
Simplicity: Users only need to connect to one gateway server, instead of managing multiple proxy lists and settings.
Scalability: Users can access a large number of IP addresses, without worrying about bandwidth limits or connection throttling.
Anonymity: Users can hide their identity and location behind real and diverse IP addresses, making it harder for websites to detect and block them.
Flexibility: Users can customize their proxy parameters, such as location, rotation time, session duration, and more, by manipulating the gateway server address.
However, backconnect proxies also have some drawbacks, such as:
Cost: Backconnect proxies are usually more expensive than regular proxies, due to the complexity and maintenance of the proxy network.
Reliability: Backconnect proxies may not always work as expected, due to the instability or unavailability of some IP addresses in the pool.
Compatibility: Backconnect proxies may not be compatible with some software or applications that require direct access to proxy servers.
Analyzing how they work
The essential difference lies in the way the proxy server is managed. Before we get to that, let’s step back and look at how the classic residential proxy works.
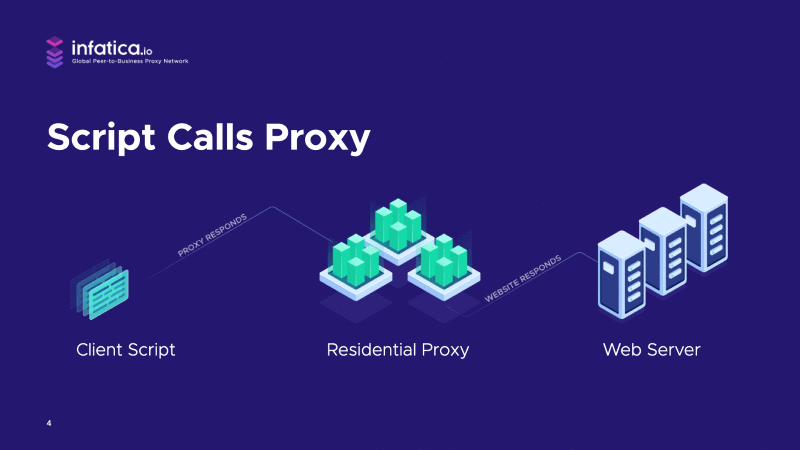
Let's say we want to crawl a website.
We have a crawling script on the left that sends a page request to the proxy server. In turn, the proxy forwards that page request to the website. The web server finds nothing unusual about the request, and serves the web page to the proxy. Completing the loop, the proxy forwards the page back to the client script.
Now, this scenario has no management layer. There is no extra layer of control between the client and the proxy. The script talks directly to the proxy, so we’ll call it “unmanaged.”
Understanding rotation and pools
There are two terms that we need to define to understand the topic better: rotation and pools. When we speak of backconnect proxies, we are really speaking of a software management layer that rotates requests from the clients out to many different proxies within a set, or “pool” of proxies.
🎯 Further reading: Exploring Rotating Proxies: Use Cases and Comparison with Static Proxies

In our example, we’ll say the pool is only made up of residential proxies, but in theory, the pool could be a mix of residential, datacenter, or even mobile proxies.
🛫 Further reading: Residential Proxies: A Complete Guide to Using Them Effectively
🚁Further reading: What Are Datacenter Proxies and When You Should Use Them
🚀Further reading: All You Need to Know about Mobile Proxies: How They Work & How to Use Them
Let’s see what that would look like:
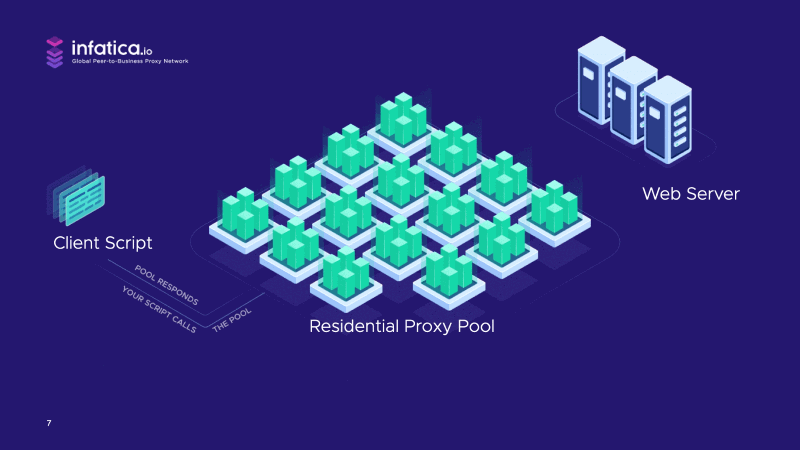
This starts out as the same use case: The client script requests a web page, but this time, it requests the page not from a single proxy, but from the entire proxy pool. That pool is managed by a software control layer that quickly considers a range of decision factors such as how many requests the last used proxy has made, and how many we want to limit it to.
The control layer decides either to use the same proxy again, or to use a fresh, different proxy with a different residential IP address. If the software decides to change IPs, we call that rotation.
Now, the selected proxy within our pool has its instructions to request a page from the website we are crawling. The web server sees nothing threatening or unusual about the request and serves the page. The same proxy in the pool forwards that page back to the client script.
That round trip shows how backconnect proxies work: They manage a pool of available proxies to rotate client requests among the members of the pool.
Unlike backconnect residential proxies, their classic counterpart is unmanaged; the client script accesses a single proxy directly.
Choosing the right tool for the job

So, why would you want to use one or the other? Backconnect proxies offer higher data throughput, allowing you to get your jobs done faster. They offer better protection against rate limiting, which is where a web server decides your IP address has made a suspiciously high number of page requests within a fixed time frame.
However, backconnect proxies are going to come at a higher price than classic residential proxies because they consume more resources to offer better scalability.
What about classic proxies?
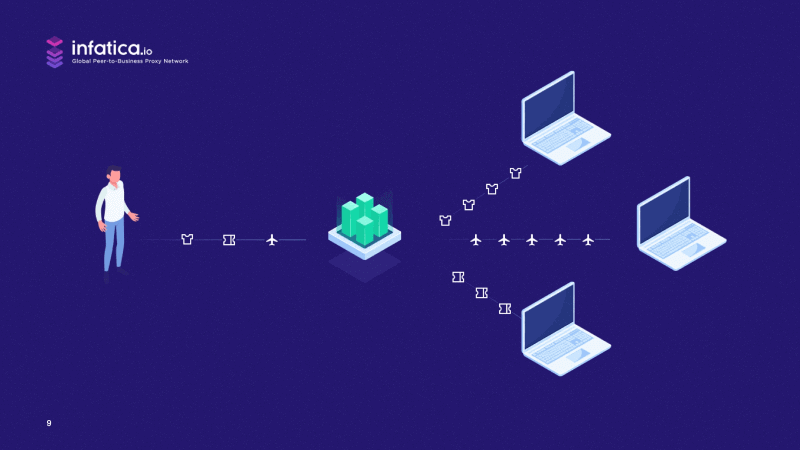
When might you prefer not to rotate proxies? A consumer trying to impersonate multiple different and credible profiles to access a single limited ecommerce offer would want to keep the same IP address for each profile.
In this scenario, we’re really talking about concert ticket purchases or sneaker copping. In these use cases, which are generally associated with individuals, using several classic proxies would make more sense than using a backconnect rotating proxies pool.
Additional benefits that backconnect proxies offer

To wrap up, let’s look at the other features and configurations backconnect proxies offer. Having more concurrent streams means capability to keep many connections alive at the same time, and the higher the number of concurrent streams, the more your backconnect package will cost.
More streams could come in handy when you are trying to crawl multiple websites at the same time. A great example of this kind of job might be a pricing aggregator website.

Another feature backconnect proxies offer is the ability to skip over IP addresses that have for one reason or another been banned by certain sites. This is rare, but it happens, so auto-skipping banned IPs speeds up your crawl rate.
Conclusion
This will wrap up our discussion of the differences between classic and backconnect proxies. Each has its own place and value. Either provides security and anonymity. The choice often comes down to which is more desired for your hobby or business: stickiness or scalability.







