
When it comes to fetching data from the web, two command-line tools stand out: wget and curl. Both are lightweight, widely available, and trusted by developers, sysadmins, and data professionals around the world. While they share some overlap, each tool was designed with different goals in mind – wget for efficient file retrieval and website mirroring, curl for flexible interactions with URLs and APIs.
In this article, we’ll compare wget and curl side by side, examining their strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases for web scraping. You’ll also see how proxies can complement these tools to create a more robust and scalable scraping setup.
What is wget?
Wget (short for “World Wide Web get”) is a command-line utility designed to retrieve files from the web. Originally developed as part of the GNU Project, wget is known for its simplicity, reliability, and focus on downloading content over HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.

One of wget’s defining features is its ability to recursively download entire websites, making it useful for tasks such as creating offline mirrors or bulk-fetching resources. It also supports resuming interrupted downloads, which is particularly handy when working with large files or unstable connections.
Key Advantages of wget
- Ease of use – straightforward syntax for downloading files and web pages.
- Recursive downloading – useful for mirroring entire websites.
- Background execution – continue downloads even after logging out.
- Robust handling of interruptions – automatic retries and resume support.
In short, wget is best suited for bulk file downloads and static website scraping, but less effective for data extraction from dynamic or API-driven sites – where curl or proxy-enabled solutions may be more appropriate.
What is curl?
Curl (short for “Client URL”) is a versatile command-line tool and library designed for transferring data with URLs. Unlike wget, which emphasizes downloading content, curl focuses on flexible communication with servers, making it especially useful for testing APIs, managing headers, and handling cookies or authentication.
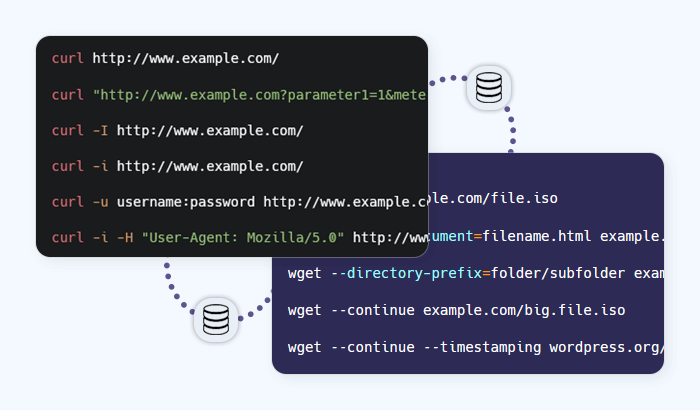
Curl supports a wide range of protocols – including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, IMAP, and more – making it a powerful tool for developers who need more than just basic file retrieval. Its flexibility has made it a standard utility in software development, network debugging, and automated data pipelines.
Key Advantages of curl
- Broad protocol support – works with many protocols beyond HTTP/HTTPS.
- Customizable requests – send headers, cookies, authentication tokens, and POST data.
- Great for APIs – widely used to test and fetch data from REST APIs.
- Interactive debugging – analyze server responses and request behavior.
Overall, curl is the go-to tool when you need precise, customizable web requests, particularly for APIs and structured data retrieval. For tasks like mirroring entire websites, however, wget often provides a simpler solution.
wget vs. curl: Key Differences for Web Scraping
Although both wget and curl can retrieve data from the web, they serve different purposes and excel in different scenarios. Wget is more efficient for simple file downloads and website mirroring, while curl offers greater flexibility for APIs and fine-tuned requests.
| Feature / Aspect | wget | curl |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use Case | File downloads, website mirroring | API interactions, custom HTTP requests |
| Ease of Use | Simple syntax for basic downloads | More complex, but highly customizable |
| Protocol Support | HTTP, HTTPS, FTP | 20+ protocols (HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, IMAP, etc.) |
| Recursive Downloading | Yes, built-in | No, requires scripts or loops |
| Header & Cookie Handling | Basic, limited flexibility | Advanced, supports custom headers, cookies, tokens |
| API Requests | Not designed for APIs | Excellent for REST and SOAP APIs |
| Automation & Scripting | Good for mirroring and batch downloads | Excellent for scripting complex requests |
| Performance | Optimized for bulk/static downloads | Optimized for precise, request-by-request interactions |
| Web Scraping Suitability | Best for simple/static scraping tasks | Best for dynamic/API-driven scraping tasks |
| Proxy Support | Yes, but basic | Yes, advanced support for different proxy types |
Takeaway:
- Use wget when you need to grab entire websites or bulk files quickly.
- Use curl when you need fine-grained control over requests, such as APIs or custom headers.
- For scaling web scraping, both tools benefit from proxy integration to avoid IP blocks and access geo-restricted content.
Limitations of wget and curl in Web Scraping
While wget and curl are powerful command-line tools, they were not built with large-scale web scraping in mind. For small, straightforward tasks, they work well – but as soon as scraping involves more complex or high-volume scenarios, their limitations become clear.
- Dynamic content: Both tools struggle with JavaScript-heavy websites, since they can only fetch static HTML.
- Session management: Handling cookies, authentication, or multi-step login processes is possible but cumbersome.
- Scalability: Sending hundreds or thousands of requests quickly may trigger rate limits or blocks.
- Anti-bot measures: Websites often deploy CAPTCHAs, IP throttling, or bot detection, which wget and curl cannot bypass on their own.
- Geo-restricted content: Accessing location-specific data requires proxies or VPNs, which neither tool provides natively.
In practice, wget and curl are best used as building blocks – tools that can handle fetching data but not the broader challenges of modern scraping. To scale up effectively, they need to be combined with proxy networks, automation frameworks, or specialized scraping tools that manage sessions, rotations, and anti-bot strategies.
How Proxies Enhance wget and curl Scraping
Both wget and curl are useful for fetching data, but their real power in web scraping emerges when paired with proxies. A proxy acts as an intermediary between your scraping tool and the target website, helping you overcome common challenges like IP blocks, rate limits, and geo-restrictions.
Benefits of Using Proxies with wget and curl
- Avoid IP bans: Distribute requests across multiple IPs to prevent detection.
- Bypass rate limits: Rotate through proxy pools to avoid throttling.
- Access geo-restricted data: Use proxies in different countries to see localized prices, content, or search results.
- Improve reliability: Reduce the risk of failed requests due to server-side blocking.
Using wget with a proxy:
wget -e use_proxy=yes -e http_proxy=http://USERNAME:PASSWORD@PROXY_HOST:PORT https://example.com
Using curl with a proxy:
curl -x http://USERNAME:PASSWORD@PROXY_HOST:PORT https://example.com
Both tools allow easy proxy integration, but the real value comes from using a reliable proxy provider that can supply a diverse pool of IPs. For instance, Infatica offers residential, mobile, and datacenter proxy networks designed specifically for large-scale scraping and data collection. By combining these proxies with wget or curl, you can scale operations, maintain anonymity, and access data without interruption.