- Proxy Types Table
- Forward Proxy
- Reverse Proxy
- Transparent Proxy
- Anonymous Proxy
- Datacenter Proxy
- Residential Proxy
- Mobile Proxy
- HTTPS (SSL) Proxy
- HTTP Proxy
- SOCKS5 Proxy
- DNS Proxy
- SMTP Proxy
- Tor Onion Proxy
- SEO Proxy
- Public Proxy
- Private Proxy
- Shared Proxy
- Static Proxy
- Rotating Proxy
- Where Do I Find Secure and Fast Proxies?
- Frequently Asked Questions


Are you looking for a way to access web pages anonymously, securely, and efficiently? If so, you might want to learn about the different types of proxies and how they work. In this article, we will explain what proxies are, why you need them, how they work with target servers, and how to choose the best proxy type for your needs. We will also introduce you to Infatica, one of the leading proxy providers that can help you achieve your online goals.
Proxy Types Table
Proxies come in all shapes and sizes – let’s group different proxy server types based on their key characteristics like location, anonymity, and use cases:
| Proxy Based on Location | Geo-restricted proxies, Geo-spoofing proxies, Local proxies, Global proxies |
| Proxy Based on Traffic Flow |
Forward proxies, Reverse proxies, DNS proxies, Tor onion proxies |
| Proxy Servers Based on Anonymity Level | Transparent proxies, Anonymous proxies, Elite proxies, Distorting proxies |
| Proxy Servers Based on Application | Web proxies, Mail proxies, SOCKS proxies, HTTPS (SSL) proxies, HTTP proxies, SMTP proxies |
| Proxy Based on Service | Public proxies, Private proxies, Shared proxies, Dedicated proxies, SEO proxies |
| Proxy Types Based on IP | Static proxies, Dynamic proxies, Rotating proxies, Mobile proxies, Residential proxies, Datacenter proxies |

Forward Proxy
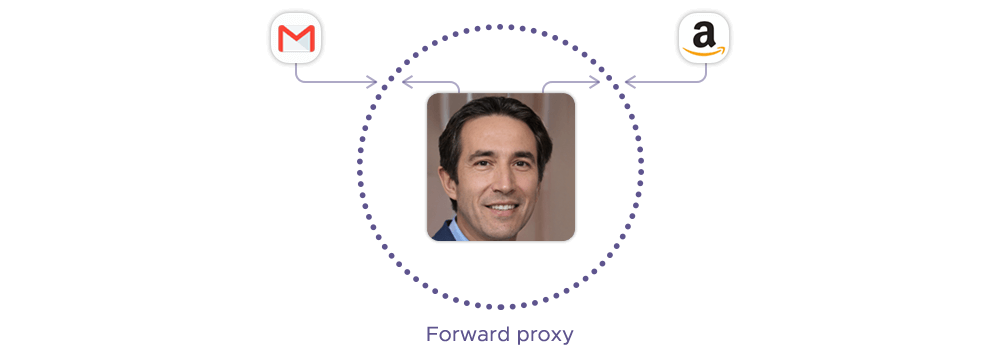
The forward type of proxy is a server that acts as an intermediary between one or more user devices and the internet. It receives requests from the user devices and forwards them to the destination web servers on their behalf. The web servers only see the IP address of the proxy, not the original user devices.
A forward proxy server gets its name from its ability to forward the user's requests to the destination web servers on their behalf. This is different from reverse proxies, which forward the web server's responses to the user's devices on their behalf. Forward proxies are mainly used for the proxy user’s privacy, policy enforcement, traffic visibility, and shadow IT detection.
Forward proxies can have various use cases, such as:
- Masking the client's IP address and location of the user devices to access geo-restricted or censored websites or services
- Filtering or modifying the requests or responses according to certain rules or policies
- Acting as a caching proxy for frequently accessed or static content to reduce bandwidth and improve performance
- Logging or monitoring the user activity or web traffic for security or auditing purposes
Reverse Proxy
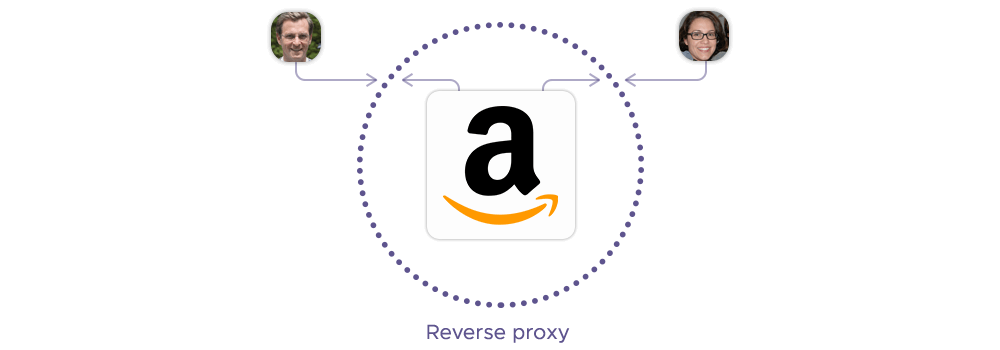
A reverse proxy server sits in front of one or more web servers, intercepting requests from clients (e.g. web browsers) and forwarding them to the web servers on their behalf. The web servers only see the IP address of the proxy, not the original clients.
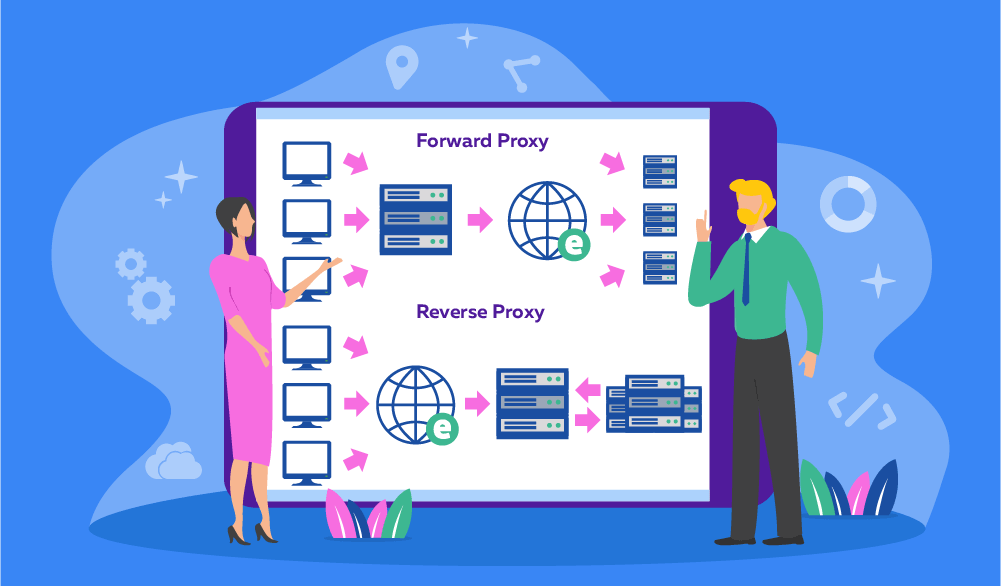
Reverse types of proxy servers are called that because they reverse the direction of the proxying process. Instead of the clients using the proxy to reach the web servers, the web servers use the proxy to reach the clients.
Reverse proxies can have various use cases, such as:
- Improving the scalability, performance, and resilience of the web servers by load balancing, caching the content, and handling failures
- Enhancing the security of the web servers by filtering malicious requests, encrypting the communication, and hiding the identity and location of the web servers
- Adding or modifying the features of the web servers by compressing the responses, rewriting the URLs, or transforming the data
Transparent Proxy
Transparent proxies intercept the connection between a user device and the internet, without modifying the requests or responses. These types of proxy servers are called "transparent" because the user device does not need to configure any proxy settings or know that the proxy exists.

A transparent proxy server can have various use cases, such as:
- Filtering or censoring content based on certain rules or policies
- Authentication gateway for accessing restricted websites or services
- Caching frequently accessed or static content to reduce bandwidth and improve performance
- Logging or monitoring the user activity or web traffic for security or auditing purposes
Anonymous Proxy

Anonymous proxies act as an intermediary between your device and the internet, without modifying the requests or responses. This type of proxy is called "anonymous" because the server does not reveal your original IP address to the website you are visiting, but instead replaces it with a new one.
Anonymous proxies provide various use cases, such as:
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the website you are visiting
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services
- Scraping data from websites that might otherwise detect and block your requests
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices
Datacenter Proxy
Datacenter proxies are hosted on servers in data centers, which are not regular internet service providers. They replace your original IP address with one temporarily leased from a data center. This type of proxy is usually faster and cheaper than residential proxies, but also easier to detect and block by some websites.
This proxy type can have various use cases, such as:
- Web scraping or data mining from websites that do not have strict anti-bot measures
- Accessing geo-restricted or censored content by changing your apparent location
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices
- Enhancing your online security and anonymity by hiding your real IP address
Residential Proxy
A residential proxy uses an IP address sourced by an internet service provider (ISP), not a data center. A residential proxy has a physical location that corresponds to the IP address. This makes it more difficult for websites to detect and block your proxy connection, as it looks like a regular user's connection.

Residential types of proxy servers are called that because they use IP addresses from residential networks, not from data centers or mobile networks. They are usually slower and more expensive than data center proxies, but also more reliable and secure. Additionally, there are proxy types like residential rotating proxy, which can change (rotate) IPs automatically.
Residential proxies can have various use cases, such as:
- Web scraping or data mining from websites that have strict anti-bot measures
- Accessing geo-restricted or censored content by changing your apparent location
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices
- Enhancing your online security and anonymity by hiding your real IP address
Mobile Proxy
This is a proxy type that uses an IP address provided by a mobile carrier, such as 4G or 5G. It makes it look like you are connected to the internet via a mobile data network, masking your real IP address.

Mobile types of proxy are called that because they use IP addresses from mobile networks, not from data centers or residential networks. They are usually more difficult to detect and block by some websites, as they look like regular user connections.
Mobile proxies can have various use cases, such as:
- Web scraping or data mining from websites that have strict anti-bot measures
- Accessing geo-restricted or censored content by changing your apparent location
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices
- Enhancing your online security and anonymity by hiding your real IP address
HTTPS (SSL) Proxy

An HTTPS (SSL) proxy is a server that uses the HTTP protocol over SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to broadcast encrypted data. An HTTPS (SSL) proxy works by intercepting the connection request from the client and establishing a secure tunnel with the web server on behalf of the client. The web server only sees the IP address of the proxy, not the original client. The proxy then forwards the request and the response between the client and the web server, encrypting and decrypting the data with SSL certificates and keys.
HTTPS (SSL) types of proxy have various use cases, such as:
- Enhancing the security and privacy of the client by hiding their identity and location from the web server and preventing eavesdropping or tampering of the data
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services by changing the apparent location of the client
- Scraping data from websites that use HTTPS protocol and have strict anti-bot measures by mimicking a regular user's connection
- Testing the functionality or performance of a website from different locations or devices by using proxies from different regions or networks
HTTP Proxy
An HTTP proxy uses the HTTP protocol to forward connection requests from you to the target website and return the requested data. The website only sees the IP address of the proxy, not your original device.
HTTP types of proxy are called that because they use the HTTP protocol, which is the standard protocol for web communication. HTTP proxies can handle both HTTP and HTTPS requests, but they do not encrypt the data, unlike HTTPS proxies.
An HTTP proxy server can have various use cases, such as:
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the website you are visiting
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services by changing your apparent location
- Scraping data from websites that do not have strict anti-bot measures
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices
SOCKS5 Proxy
SOCKS5 types of proxy are called that because they use the SOCKS protocol, which is a network protocol that allows applications to exchange data through a proxy server. SOCKS stands for Socket Secure, and SOCKS5 is the latest version of the protocol. SOCKS5 supports both TCP and UDP protocols, as well as various authentication methods.
A SOCKS5 proxy server can have various use cases, such as:
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the website you are visiting
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services by changing your apparent location
- Scraping data from websites that have strict anti-bot measures by mimicking a regular user's connection
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices by using proxies from different regions or networks
DNS Proxy

A DNS proxy is a server that forwards a DNS request from the user to DNS servers. DNS stands for Domain Name System, which is a system that translates domain names (like infatica.io) into IP addresses (like 151.101.2.114) that computers can understand.
DNS types of proxies work by intercepting the DNS request from the user and sending it to a different DNS server than the one assigned by the user's ISP. The DNS server then returns the IP address of the requested domain to the user, allowing them to access the website or service. The DNS proxy can also modify the IP address to spoof the user's location or bypass geo-restrictions or censorship.
Smart DNS proxies have various use cases, such as:
- Accessing geo-restricted or censored content by changing the apparent location of the user
- Improving the speed and performance of the DNS resolution by using a faster or closer DNS server
- Enhancing the security and privacy of the user by hiding their original DNS server and preventing DNS hijacking or spoofing
- Testing the functionality or performance of a website from different locations or devices by using proxies from different regions or networks
SMTP Proxy
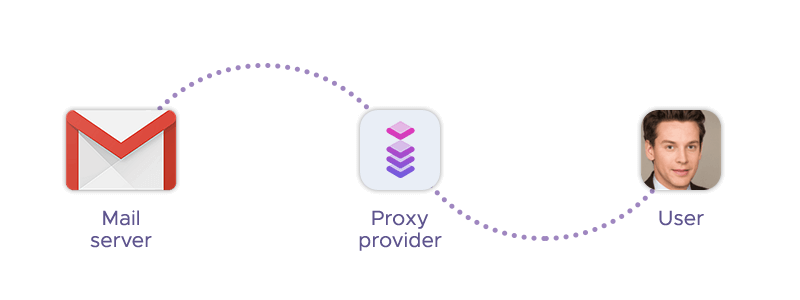
An SMTP proxy forwards SMTP sessions from you to the destination mail server on their behalf. SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol, which is a protocol for sending and receiving email messages. An SMTP proxy is also called a mail proxy or a mail relay.
An SMTP proxy works by intercepting the SMTP connection request from your device and initiating another SMTP connection to the destination mail server. The mail server only sees the IP address of the proxy, not your original device. The proxy then forwards the SMTP commands and data between your device and the mail server, without storing or modifying the messages.
The SMTP types of proxies has various use cases, such as:
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the mail server and preventing eavesdropping or tampering of the messages
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain mail servers or services by changing your apparent location
- Filtering or modifying the messages according to certain rules or policies, such as spam filtering, virus scanning, or DKIM signing
- Improving the scalability, performance, and resilience of the mail servers by distributing the load, caching the content, and handling failures
Tor Onion Proxy
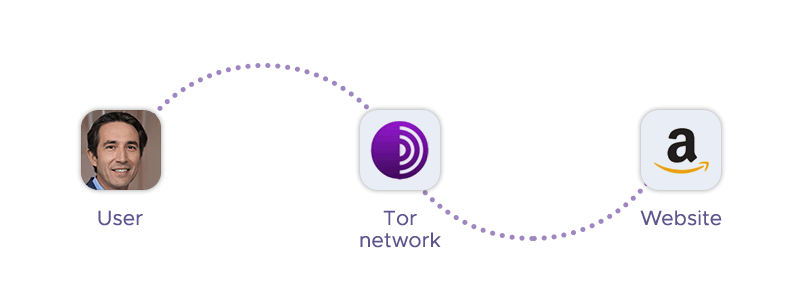
A Tor onion proxy is a server that acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, using the Tor network to forward connection requests from you to the target website and return the requested data. The website only sees the IP address of the proxy, not your original device.
Tor onion proxies are called that because they use Tor, which is a high-anonymity proxy network that routes your web traffic through a series of relays or nodes. Tor stands for The Onion Router, and each relay adds a layer of encryption to your data, like the layers of an onion. Tor onion proxies can handle both HTTP and HTTPS requests, and they encrypt the data with SSL certificates and keys.
The Tor types of proxies have various use cases, such as:
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the website you are visiting and preventing eavesdropping or tampering of the data
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services by changing your apparent location
- Scraping data from websites that have strict anti-bot measures by mimicking a regular user's connection
- Accessing .onion sites, which are hidden services that can only be reached through the Tor network
SEO Proxy

SEO proxies are online servers that enable you to browse the internet without revealing your real IP address or location. The proxy server acts as a bridge between your website and your device. SEO proxies help you anonymize your SEO research and avoid access restrictions when using SEO tools or scripts.
The SEO proxy type can have various use cases, such as:
- Web scraping or data mining from websites that have strict anti-bot measures
- SEO monitoring and keyword research by accessing local or global search data
- Link building and CPA manipulation by creating multiple accounts or posting comments
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices
Public Proxy
Public proxies are called that because they are free and open to multiple users, meaning anyone can use them without any authentication or registration. However, this also means that public proxies are often far less effective, reliable, and secure than private proxies.
The public proxy type can have various use cases. However, keep in mind that the nature of these unreliable proxies makes it hard to perform these tasks efficiently.
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the website you are visiting
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services by changing your apparent location
- Scraping data from websites that do not have strict anti-bot measures
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices
Private Proxy
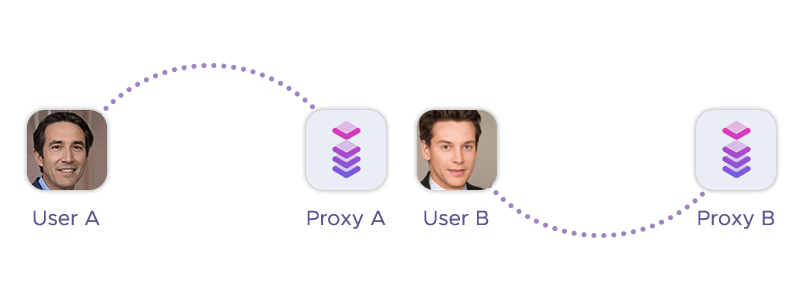
This proxy type gets its name from the fact that it’s not free and open to the public, meaning only you or a limited number of users can use them with authentication or registration. This also means that private proxies are often more effective, reliable, and secure than public proxies.
Private proxies can have various use cases, such as:
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the website you are visiting
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services by changing your apparent location
- Scraping data from websites that have strict anti-bot measures
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices
Shared Proxy
A shared proxy is an internet server that acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, forwarding connection requests from you to the target website and returning the requested data. The website only sees the IP address of the proxy, not your original device.
The shared proxy type is called that because it’s not not dedicated to a single user, but shared among multiple users simultaneously. This means that the same IP address can be used by different users at the same time.
Shared proxies can have various use cases, such as:
- Reducing the cost of proxy services by splitting the price among multiple users
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the website you are visiting
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services by changing your apparent location
- Scraping data from websites that do not have strict anti-bot measures
Static Proxy
The static proxy type is a server that acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, using a fixed IP address that does not change over time. This is in contrast to dynamic proxies, which use a rotating pool of IP addresses that change frequently.
Static proxies can have various use cases, such as:
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the website you are visiting
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services by changing your apparent location
- Scraping data from websites that do not have strict anti-bot measures
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices
Rotating Proxy
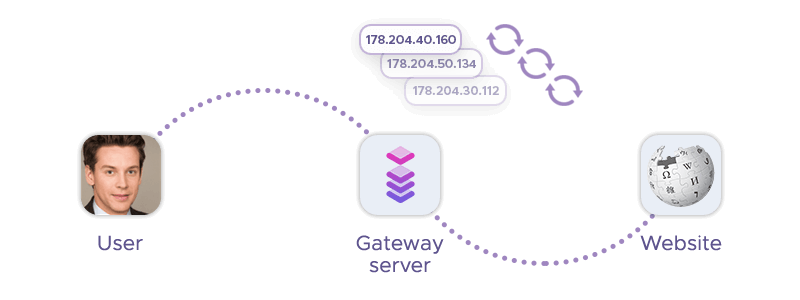
A rotating proxy is a server that acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, forwarding connection requests from you to the target website and returning the requested data. The website only sees the IP address of the proxy, not your original device.
This proxy type gets its name from a pool of IP addresses that change frequently, either after every connection or after a set period. This makes it more difficult for websites to detect and block your proxy connection, as it looks like a different device or location each time.
Rotating proxies can have various use cases, such as:
- Enhancing your online privacy and security by hiding your identity and location from the website you are visiting
- Bypassing geo-restrictions or censorship that might block access to certain websites or services by changing your apparent location
- Scraping data from websites that have strict anti-bot measures by mimicking a regular user's connection
- Testing the functionality or performance of your website from different locations or devices by using proxies from different regions or networks
Where Do I Find Secure and Fast Proxies?
If you are looking for a reliable and affordable proxy service, you might want to check out Infatica. Infatica is a global provider of proxy services, offering residential, mobile, and datacenter proxies for businesses and individuals. These services are used for a variety of purposes, including web scraping, data collection, brand protection, and improving online privacy.
Infatica stands out as a top-tier provider, offering different types of proxies with a remarkable success rate, perfectly catering to technical demands. Their robust infrastructure and proven expertise make them a preferred choice for businesses seeking high-performance proxy solutions. Infatica also offers a web scraper API, which allows you to scrape data from any website without worrying about CAPTCHAs, IP blocks, or JavaScript rendering.
Infatica has a simple and transparent pricing model, which lets you choose between fixed monthly pricing per IP address or pay per GB for residential and mobile proxies. You can also enjoy the features available in the dashboard, such as checking your IP list, triggering rotation, changing your geolocation, and more. Infatica also provides a free trial period and a dedicated customer support team to help you with any issues or questions.
Final Words
There are many types of proxies, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. You should consider your goals, budget, and level of anonymity when choosing a proxy type. If you are looking for a reliable and affordable proxy service, we recommend you check out Infatica, a global provider of different types of proxies. Infatica can help you access geo-restricted or censored content, scrape data from websites, test your website from different locations, and enhance your online privacy and security.