- What Is a Transparent Proxy?
- How Does a Transparent Proxy Work?
- Transparent Proxy vs. Non-Transparent Proxy
- Transparent Proxies and Forced Proxies
- Business Use Cases for Transparent Proxy
- Pros and Cons of Transparent Proxies
- How To Detect a Transparent Proxy
- How To Bypass a Transparent Proxy
- Which Transparent Proxy Settings Can You Modify?
- Frequently Asked Questions


A transparent proxy is an essential tool for anyone who wants to access the internet securely and efficiently. They can help users bypass censorship, protect their identity, improve performance, and access geo-restricted content. However, not all proxies are the same. Some proxies are more transparent than others, meaning that they do not alter requests and responses between the user and the website. In this article, we’re tackling the “what is a transparent proxy?” question: You’ll learn how transparent proxies work, what are some of its use cases, and what are its pros and cons. You will also learn how to set it up and how to protect yourself from unwanted transparent proxies.
What is a transparent proxy?
A transparent proxy is a server that intercepts web traffic and doesn’t modify requests in the process. It acts as a server position between a user's device and the website they are trying to access. In various definitions, it is also known as an inline proxy, intercepting proxy, invisible proxy server, or forced proxy. It can be installed without your knowledge and without any software or configurations on your part. The proxy is called “transparent” because it does not mask the user's IP address, enabling websites to read it.

How Does a Transparent Proxy Work?
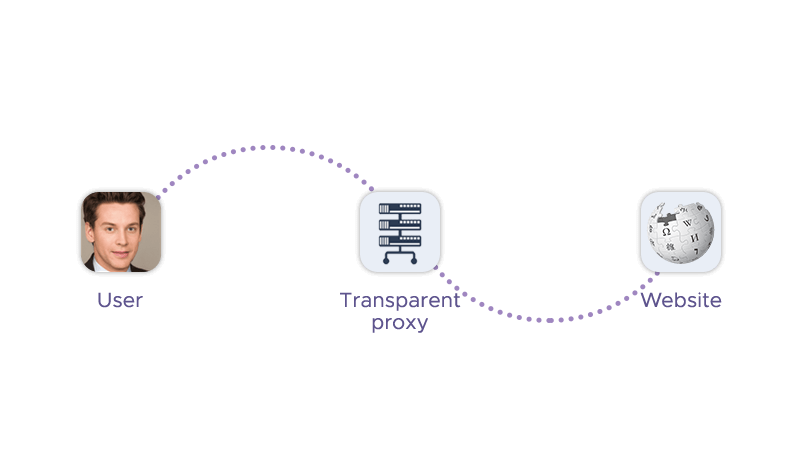
A transparent proxy server works by intercepting the communication between a client and the internet without requiring any special client-side configuration or knowledge. It can be installed by a webmaster or an internet service provider (ISP) without users knowing. Using a proxy typically involves configuring your network routing to redirect traffic to the proxy server. This process varies depending on the specific router and the proxy software. The proxy server then forwards the requests and responses without modifying them, except for adding the user's IP address and the fact that it is a proxy to the HTTP header. Similarly to an ordinary proxy, it can also perform various functions such as content filtering, security, caching, etc., based on its settings.
What are the characteristic features of a transparent proxy?
| Feature | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Automatic Proxy Detection | Transparent proxies can automatically detect and configure the appropriate proxy settings for each client without requiring manual setup. This simplifies the process for end-users, as they do not need to alter their browser or system settings. |
| Seamless Integration with Network Infrastructure | They are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing network infrastructure, allowing for easy deployment and minimal disruption to current operations. |
| Improved Network Performance | Transparent proxies can cache frequently accessed content, reducing the load on the network and speeding up response times for the end-users by serving cached content instead of retrieving it from the original source each time. |
| Simplified Management of Traffic | These proxies can simplify traffic management by providing a single point of control for all outgoing web traffic. This allows for easier monitoring, logging, and enforcement of company policies. |
Transparent Proxy vs. Non-Transparent Proxy
The difference between a transparent and non-transparent proxy is that the former server does not modify requests, or hide settings, while the latter does. The former also reveals the user's IP address and the fact that it is a proxy to the destination server, while non-transparent proxies can mask the user's IP address and appear as a regular user. Last but not least, a non-transparent proxy requires manual configuration of the firewall on client devices. Both types of proxies can be used for different purposes, such as content filtering, security, caching, etc.
Transparent Proxies and Forced Proxies
A transparent proxy is sometimes referred to as a “forced proxy” because it can be implemented without the consent or knowledge of the users. This means that a network administrator, Internet Service Provider (ISP), or webmaster can set up a transparent proxy to intercept and direct incoming traffic without requiring any configuration changes via the user’s proxy settings. The term "forced" highlights the lack of greater control or choice the user has in this scenario.
Some websites maintain unofficial proxy lists to inform users that their internet activity might be monitored through these proxies. These lists are not officially sanctioned but serve as a resource for those who want to know if their online activities are being intercepted and potentially scrutinized.
Business Use Cases for Transparent Proxy

Some of the use cases of a transparent network proxy are:
1. Filtering or Censoring Content
Here's how transparent proxies function for content filtering or censoring:
- Blocking Access: Governments, schools, and businesses configure them to block domains in the adult/gambling sphere or torrenting services.
- Monitoring Internet Activity: These proxies can monitor and log users' internet activity. This capability is often used for compliance with legal or security policies, ensuring that users are not engaging in activities that could harm the network or violate regulations.
- Enforcing Policies: By filtering content, transparent proxies help enforce company or institutional policies regarding acceptable internet use. This can include blocking websites that contain dangerous material or could lead to time-wasting during work or school hours.
- Security Measures: In addition to content filtering, they can be used to detect suspicious requests and error messages that may indicate a cyber-attack, such as a Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack. As they identify and deny requests, proxies contribute to the overall security of the network.
2. Authentication Gateway
Transparent proxies are often utilized as an authentication gateway in various network environments. Here's how they function in this role:
- Intercepting Requests: When a user attempts to access a resource, the transparent proxy intercepts the request. This is done seamlessly, without the user's knowledge, as the proxy is 'transparent' in the communication path between the user and the internet.
- Requesting Login Credentials: After intercepting the request, the proxy may redirect the user to a login page. This is a common experience when you're redirected to a web page other than the one you were trying to access, specifically to enter authentication information.
- Verifying Access Rights: The proxy will then verify the right to access via an authentication server. If the credentials are valid, the proxy confirms that the user has the right to access the requested resource.
- Allowing Access: Once the user's access rights are verified, the proxy allows the request to proceed to the intended destination. If the credentials are invalid or the user does not have the necessary permissions, the proxies restrict the access.
3. Web Caching
Web caching is a significant use case for this proxy type. Here's how it contributes to web caching:
- Data Storage: Transparent proxies store data that users are likely to access again in the near future. This includes web pages, images, CSS, and JavaScript files.
- Bandwidth Reduction: By caching content, they reduce the amount of bandwidth required from the Internet Service Provider (ISP) as users try to access content on the internet.
- Performance Improvement: When a user requests a cached resource, the proxy can serve it directly from its local cache instead of retrieving it from the original source. This speeds up the loading times for the user.
- Network Efficiency: Caching frequently accessed content on the proxy server means latency reduction and less direct traffic to the content's original servers, which can help in managing network traffic more efficiently.
4. Securing or encrypting email content
Transparent proxies can play a crucial role in securing or encrypting email content. Here's how they are used in this context:
- Inspecting Email Content: These proxies can inspect the content of emails as they are sent and received by the end user. This allows the proxy to check for malicious or suspicious content, such as malware, spam, or phishing links.
- Discarding Dangerous Emails: If the transparent proxy detects any dangerous content within an email, it has the capability to discard it, thereby preventing potentially harmful communication from reaching the user.
- Encrypting Emails: To protect the confidentiality of email content, they can encrypt emails so that they cannot be read by intruders or third parties. This encryption ensures that even if the emails are intercepted, they remain unreadable without the proper decryption key.
- TLS and SMTP Proxies: The use of Transport Layer Security (TLS) in conjunction with transparent Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) proxies represents a sophisticated approach to safeguarding email traffic. This method not only encrypts data but also ensures integrity and confidentiality, thereby mitigating risks associated with data breaches and cyber threats.

5. Preventing or mitigating DDoS attacks
Proxies help in mitigating DDoS attacks in the following ways:
- Acting as a Buffer: They act as a buffer between clients and the internet, filtering out malicious or excessive requests that could overwhelm target servers.
- Load Balancing: They can distribute the load among multiple servers, preventing congestion and downtime during an attack.
Pros and Cons of Transparent Proxies
A transparent HTTP proxy has some pros and cons, depending on how they are used and by whom. Here are some of them:
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| Easy deployment: Since they do not require any client-side configuration, they are easy to deploy and manage. Users can enjoy the benefits of a proxy without having to manually configure their devices. | Lack of anonymity: Transparent proxy servers do not hide IP addresses or the fact that they are using a proxy, exposing their identity and location to the destination server. This can compromise the user's privacy and security, especially if the destination server is malicious or untrustworthy. |
| Network optimization: They can improve network performance by caching frequently accessed content, reducing latency and bandwidth consumption. They can also balance the load among multiple web servers, preventing congestion and downtime. | Limited support: They do not support all protocols or ports, such as HTTPS, FTP, or SOCKS. This can limit the user's access to certain websites or services that use these protocols or ports. |
| Content filtering: They can block or modify unwanted traffic or content, such as malware, spam, ads, or inappropriate websites. They can also enforce internet usage policies in schools or workplaces to prevent users from accessing unauthorized or distracting websites. | Vulnerability to attacks: Transparent proxies are susceptible to SSL stripping attacks, which downgrade HTTPS connections to HTTP, allowing attackers to intercept and modify the data in transit. They are also vulnerable to DNS spoofing attacks, which redirect users to fake websites by altering DNS records. |
| Security: They can protect the network from external threats, such as DDoS attacks, by detecting and filtering suspicious requests. They can also monitor and encrypt email content, preventing intruders from reading or tampering with it. | Additional resources: They require additional hardware or software to implement, which can increase the cost and complexity of the network. They can also slow down the network performance if not configured properly or if overloaded with requests. |
Is a transparent proxy safe?
This proxy type can be safe for transmitting sensitive information, such as credentials, under certain conditions. Here are some key points to consider:
Security Measures: If the proxy has robust security measures in place, it can safely handle sensitive data. This includes proper encryption protocols to prevent data leaks.
Risk of Interception: Since proxies do not typically encrypt or modify user requests, there is a risk that data could be intercepted or tampered with during transmission. This could potentially expose sensitive information to an insecure network environment.
Dependence on Implementation: The safety of transmitting sensitive data over this proxy type largely depends on how the proxy is implemented and managed. If not secured properly, there is a potential for sensitive information to be compromised.
HTTPS and Encryption: For a higher level of security, it's recommended to use HTTPS transparent proxies, which can encrypt the content of web requests, including sensitive data, to protect against eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
How To Detect a Transparent Proxy
There are a few methods that can help you detect a proxy and determine if something is performing traffic rerouting on your end. Here are some ways to detect it:
- Invalid URL Test: Attempt to connect to a server or URL you know does not exist. If you're behind a proxy, you might not see a typical error message in your browser.
- HTTP Response Headers: Inspect the HTTP headers you receive from a website. Look for headers like X-Forwarded-For or Via, which can indicate the presence of a proxy.
- Proxy Detection Tools: Use online proxy detection tools. These tools can analyze your connection for signs of a proxy.
How To Bypass a Transparent Proxy
To bypass a proxy, you would typically use methods that counter the scenarios when the transparent proxy intercepts or modifies your internet traffic. Here are some common strategies:
- Use a VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts all traffic leaving your device, including HTTP(S) and DNS traffic. Using a different network with encryption prevents the proxy from seeing the contents or destination of your data, effectively bypassing its filtering or caching mechanisms.
- HTTPS: Using HTTPS ensures that the user connects to a website with an encryption. This can prevent the proxy from caching or altering your requests, as the data is encrypted end-to-end between your browser and the website's server.
- ISP Contact: If your Internet Service Provider is using transparent proxying, you might want to contact them and ask to be routed outside of it. However, ISPs may refuse such requests due to technical reasons.
- Proxy Detection Tools: Some tools can detect the presence of a proxy and may offer options to bypass it. These tools can be found online and can provide specific instructions based on your network setup.
Which Transparent Proxy Settings Can You Modify?
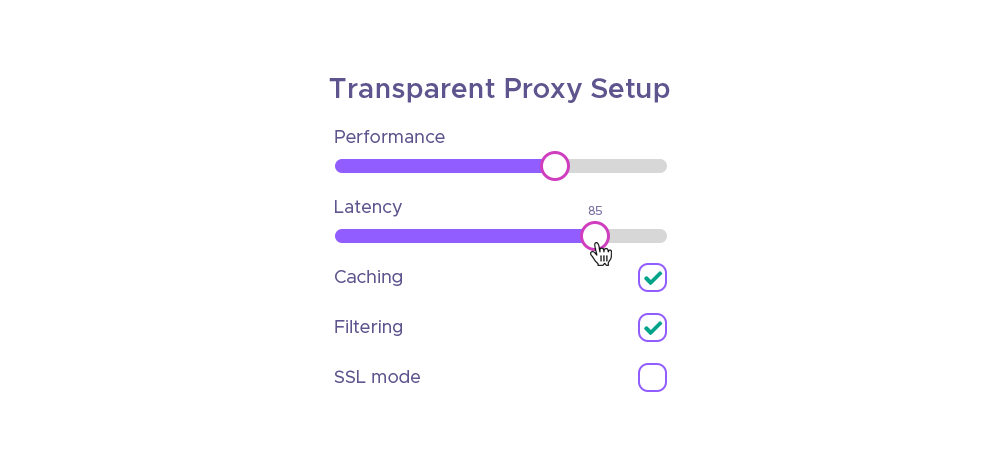
Some of the settings that this proxy type offers are:
- Interception: Specifies whether the proxy should intercept traffic at the operating system or router level.
- Authentication: Supplies the server with the same credentials as the proxy users.
- Caching: Specifies whether or not the proxy server should cache content for returning users.
- Reverse proxy: You can place the proxy in front of a web server to accelerate performance for users (as opposed to setting it to intercept remote access).
- Filtering: You can configure the proxy not to allow users to access certain protocols or ports, such as chat, data streaming, torrent threads, etc.
- Enable SSL mode: You can enable SSL encryption for your web traffic to prevent the proxy from snooping or tampering with your data. You also need to set the CA to use for this mode.
- SSL no bump sites: You can specify the sites that you do not want to bump and keep their original security layer intact, such as e-banking or other sensitive websites.
Conclusion
You’ve learned how a transparent proxy works: It is a server that can intercept and filter internet traffic without changing requests and responses. It can be used for various purposes, such as content filtering, gateway proxy, caching, reverse proxies, DDoS protection, and secure email. However, proxying also has some drawbacks, such as exposing the user's IP address, reducing privacy, slowing down performance, and potentially blocking access to legitimate content. Therefore, users should be aware of the presence and settings of proxies on their network and use encryption if needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
You can also learn more about:
- Mail us at: sales@infatica.io









