- What are datacenter proxies?
- Datacenter proxies' pros and cons
- What are residential proxies?
- What are ethical residential proxies?
- Residential proxies' pros and cons
- How Infatica’s proxies help with web scraping and data collection
- Datacenter vs. residential proxies: comparison table
- What proxies should you use for your business?
- Differences between residential, ISP, and DC proxies
- Frequently Asked Questions


The datacenter vs residential proxies comparison is crucial to get right: If you are looking for a way to improve your online security, privacy, and performance, you may want to consider using a proxy server – but which type? Not all proxies are the same. There are different proxy types, such as datacenter proxies, residential proxies, and ISP proxies, that have Both residential and datacenter proxies can help you access geo-restricted content, protect your online identity, and improve your online security – but they have different features, advantages, and disadvantages.
In this article, we analyze the difference between residential and datacenter proxies and help you choose the best one for your needs and goals. We will also explain what ethical residential proxies are and why they are more reliable, secure, and legitimate than other types of proxies.
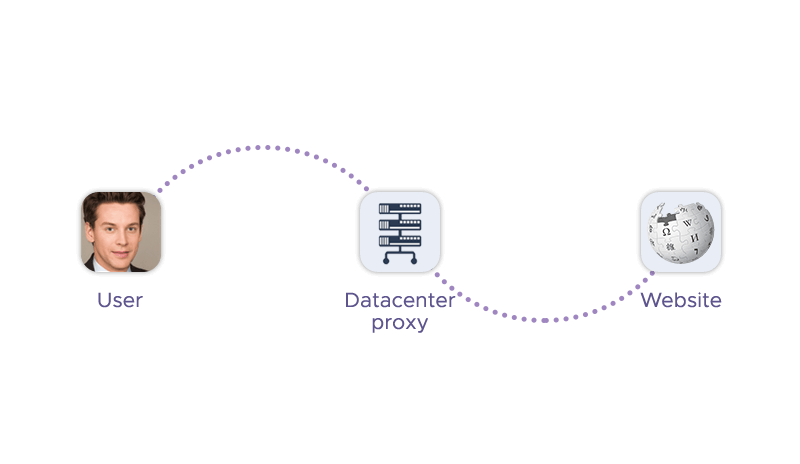
What are datacenter proxies?
Datacenter proxies are IP addresses that are hosted in servers of cloud or web hosting companies. They are not associated with any physical location or internet service provider (ISP). They are usually created in large batches and assigned to different users or customers. A datacenter proxy can offer high-speed connections, stable performance, and low costs.
Shared datacenter proxies are used by multiple users at the same time. They are more cost-effective than dedicated datacenter proxies, but they also have some drawbacks. For example, shared proxies can be easily detected and blocked by some websites, they can have lower performance and reliability, and they can pose a security risk if the other users are malicious. Shared datacenter proxies are suitable for simple tasks that do not require high anonymity or speed – using them with web scraping tools may not provide best results.
On the other hand, dedicated datacenter proxies are assigned to a single user or customer. They offer enhanced performance, faster connection speeds, and increased reliability, since the actual IP address is not shared with other users. They also provide more control and security over the proxy activity. Dedicated datacenter proxies are ideal for complex tasks that require high anonymity or speed, such as web scraping, cybersecurity, or email protection.
Datacenter proxies' pros and cons
Datacenter proxies boast these advantages:
- They offer high-speed connections, as these proxies operate via dedicated servers with high bandwidth that can handle large-scale tasks and high traffic volumes.
- Generally, datacenter proxies work in a more stable way as they are less likely to experience downtime, errors, or fluctuations than residential proxies.
- Datacenter proxies offer more flexibility and features, such as shared or private IPs, rotating or static IPs, and custom subnets or domains.
However, they can also be easily detected and blocked by target sites that have strict anti-bot measures, as they often share the same subnetwork or domain name. Datacenter proxies are suitable for tasks that require fast and reliable web scraping, such as market research, SEO monitoring, or price comparison.
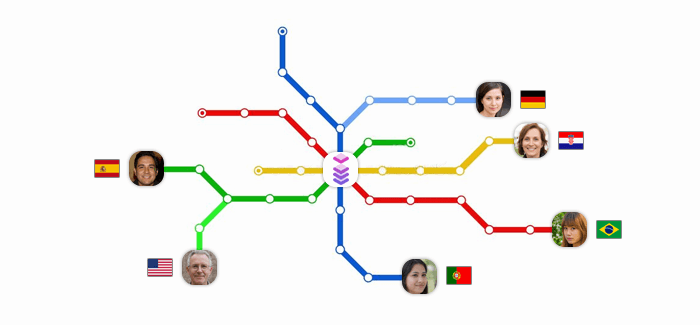
What are residential proxies?
A residential proxy is an IP address that belongs to real devices, such as computers, smartphones, or smart TVs, and are provided by ISPs. Residential proxies are associated with a specific geographic location and a real user. They are usually obtained through peer-to-peer networks or software development kits (SDKs) that allow device owners to share bandwidth of their physical devices. In return, they receive benefits, such as free access to certain apps or services. Residential proxies can offer high anonymity levels, secure browsing, and geo-targeting capabilities.
What are ethical residential proxies?
Ethical residential proxies belong to real devices and are IP addresses provided by an internet service provider (ISP). The main difference lies in the full consent and compensation of the device owners. They are obtained through transparent agreements that inform the users about their participation in the proxy network and reward them for sharing their bandwidth. Ethical residential proxies are more reliable, secure, and legitimate than other types of proxies, as they can bypass most anti-bot measures and filters and protect the privacy and online identity of both the proxy users and the device owners.
Residential proxies' pros and cons
Residential proxies offer these key features:
- They provide secure browsing, as they protect your privacy and online identity from hackers, trackers, and malicious websites.
- Residential proxies offer high anonymity levels. They use real IP addresses from internet service providers to appear as regular users – this allows them to bypass most anti-bot measures and filters.
- They enable geo-targeting capabilities. They can offer residential IPs from almost any country or city in the world, allowing you to perform ad verification, test local markets, or collect data.
However, residential proxies can also be expensive, slow, and unstable, as they depend on the availability and bandwidth of the device owners. Residential proxies are suitable for tasks that require high stealth and legitimacy, such as social media management, ad verification, or web scraping.
How Infatica’s proxies help with web scraping and data collection
Infatica offers both residential and datacenter proxies. Choose Infatica as your proxy provider – and enjoy these benefits:
- You can choose residential proxies from over 100 geolocations across North America, South America, Europe, and Asia.
- You can access over 10 million residential IP proxies that use HTTP/SOCKS protocols.
- You can have an unlimited number of concurrent sessions with persistent connections and cookies.
- You can enjoy high performance with 99.9% success rate and 0.7s average response time.
- You can optimize your web data scraping with fewer IP bans and CAPTCHAs thanks to rotating residential proxies and new IP addresses.
- You can use the API for easy user management and integration with third-party proxy management software.
- You can find flexible pricing plans for small-, medium-, and large projects with a 3-day trial.
- You can get 24/7 support from our expert team anytime you need it.
- You can access extensive documentation with proxy lists, authorization methods, location and rotation settings, and more.
Datacenter vs. residential proxies: comparison table
Residential and datacenter proxies have different characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages that make them suitable for different purposes. Let’s take a look at this datacenter vs residential proxies comparison table:
| Criteria | Residential Proxies | Datacenter Proxies |
|---|---|---|
| Source IP | Residential proxies are IP addresses that belong to real devices connected to residential networks. They are associated with a specific location and ISP. | Datacenter proxies are IP addresses that are hosted in servers of cloud or web hosting companies. They are not associated with any particular location or internet service provider (ISP). |
| Use cases | Residential proxies are commonly used for web scraping, data extraction, and market research. They can help web scrapers to bypass anti-scraping measures and access geo-restricted content without being blocked or banned by the target websites. | Datacenter proxies are commonly used for online anonymity, privacy, and security. They can help users to get an alternate IP address and location, access geo-blocked or censored content, and protect their identity from hackers, trackers, or malicious actors. |
| Proxy anonymity level | Residential proxies have a high proxy anonymity level. They can mimic organic traffic and appear as real users to most websites thanks to residential IPs. | Datacenter proxies have a low proxy anonymity level. They can be easily detected and identified as proxies by some websites that use advanced proxy detection techniques. |
| IP Blocking and Detection | Residential proxies have a lower risk of IP blocking and detection. Since they use real IP addresses from residential networks, they can blend in with the normal traffic and avoid raising any red flags to the target websites. However, residential proxies can still be blocked or detected if they abuse the website’s terms of service or request rate limits. | Datacenter proxies have a high risk of IP blocking and detection. Since they are usually created in large batches and assigned to different users or customers, datacenter IPs can share the same IP subnetworks or domains. This makes them more noticeable and suspicious to the target websites, which can block or blacklist datacenter proxies if they detect any abnormal or malicious activity. |
| Speed and Reliability | Residential proxies have lower speed and reliability. They offer slower connection speeds, and variable performance since they depend on the availability and condition of the real devices and residential proxy providers. | Datacenter proxies have high speed and reliability. They offer fast connection speeds, stable performance, and consistent quality, since data center IPs are hosted in servers with dedicated bandwidth and resources. |
| Scalability | Residential proxies have lower scalability. They can be hard to obtain, manage, or control in large numbers due to the limited proxy pool and diversity of the real devices and networks that provide them. | Datacenter proxies have high scalability. More IP addresses can be easily created and then modified or deleted in large quantities according to the user’s needs and preferences. |
| Security | Residential proxies have high security. They can provide a secure connection between the user and the target website, since the user’s data and activity are encrypted and routed through real devices that belong to verified individuals or companies. | Datacenter proxies have low security. They can pose a security risk if the user shares the same IP address with other users who are malicious or compromised. The user’s data and activity can be exposed, intercepted, or manipulated by hackers, trackers, or malicious actors who have access to the same data center. |
| Cost | Residential proxies have high cost. They are more expensive than datacenter proxies because they are harder to obtain and manage. | Datacenter proxies have low cost. They are cheaper than residential proxies because they are easier to create and maintain. |
What proxies should you use for your business?

Choosing the right type of proxy for your business depends on several factors, such as your goals, budget, and requirements. Datacenter and residential proxies have different pros and cons that make them suitable for different purposes. Let’s analyze some of the factors that you should consider when choosing between datacenter and residential proxies.
Goals: What are you trying to achieve with proxies? If you are looking for online anonymity, privacy, and security, datacenter proxies might be a good option for you. They can help you to hide your real IP address and location from the websites you visit, access geo-restricted content, and protect your identity from hackers, trackers, or malicious actors. However, if you are looking for web scraping, data extraction, and market research, residential proxies might be a better option for you. They can help you to bypass anti-scraping measures and access geo-restricted content without being blocked or banned by the target websites.
Budget: How much are you willing to spend on proxies? Datacenter proxies are cheaper than residential proxies because they are easier to create and maintain. However, they also have lower quality and performance. Residential proxies are more expensive because they are harder to obtain and manage. However, they also have higher quality and performance than datacenter proxies.
Requirements: What are your specific needs and preferences for proxies? Datacenter proxies offer high speed and reliability, low cost, high scalability, and low security. Residential proxies offer lower internet connection speed and reliability, high cost, low scalability, and high security. Depending on your requirements, you can choose the type of proxy that best suits your needs. For example, if you need faster proxies, stable performance, and consistent quality, a datacenter proxy might be a good choice for you. However, if you need a high anonymity level, low risk of IP blocking and detection, and secure connection, a residential proxy might be a better choice for you.
Use cases: Both datacenter and residential proxies feature a large number of scenarios. You would typically use a datacenter proxy for:
- Scraping data from e-commerce websites, minor search engines, or access content from other websites that have low security levels
- Bypassing IP address bans, as they can change your IP address with a new one
- Accessing geo-restricted content, if they have servers in different locations
- Performing market research, SEO analysis, or price comparison
You can utilize residential proxies for:
- Using web scrapers to collect data from various online sources without being detected or blocked by anti-bot measures or filters
- Accessing geo-restricted content, such as streaming services, online shopping, or social media platforms
- Managing multiple social media accounts without triggering security systems or violating terms of service
- Testing local markets, conducting web scraping, or protecting your privacy and online identity
Differences between residential, ISP, and DC proxies

ISP proxies are different from datacenter and residential proxies in several ways. Here are some of the main differences:
DC vs. ISP proxies: ISP proxies are IP addresses that are registered under internet service providers (ISPs), such as Comcast, Verizon, or AT&T. Datacenter proxies are IP addresses that are hosted in servers of cloud or web hosting companies, such as Amazon, Google, or Microsoft. Residential proxies are IP addresses that belong to real devices, such as computers, smartphones, or smart TVs, and are provided by ISPs.
ISP proxies are as fast and stable as datacenter proxies, as they have dedicated servers and high bandwidth that can handle large-scale tasks and high traffic volumes. Datacenter proxies are also fast and stable, but they may have some drawbacks, such as low anonymity, easy detection, or shared IPs.
Residential vs ISP proxies: ISP proxies are harder to detect and less prone to IP bans than datacenter proxies, as they appear as regular users and can bypass most anti-bot measures and filters. Residential proxies are also hard to detect and block, but they may have some drawbacks, such as slow speed, unstable performance, or limited control.
ISP proxies don't need to rotate, so they're very handy for tasks that require a consistent identity, such as social media management or running sneaker bots. Datacenter proxies may also offer static IPs, but they may not work well with some websites that have strict security measures. Residential proxies usually rotate frequently, which can be useful for tasks that require a high level of anonymity, such as web scraping or data mining.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about the differences between datacenter and residential proxies. We have seen that datacenter proxies are IP addresses provided by web hosting companies that offer high-speed connections, stable performance, and low costs, but that can also be easily detected and blocked by websites that have strict anti-bot measures. We have also seen that a residential proxy provides IP addresses that belong to real devices and are provided by ISPs, that offer high anonymity levels, secure browsing, and geo-targeting capabilities, but that can also be expensive and unstable. See you in the next article!