
In today's data-driven world, businesses of all sizes are increasingly turning to data as a service (DaaS) to harness the power of information. By abstracting the complexities of data management, DaaS allows companies to focus on extracting actionable insights and optimizing operations. In this article, we’ll explore the workings of a DaaS pipeline, the numerous benefits it offers, challenges to consider, and its application across various industries, illustrating how DaaS is transforming the landscape of modern business.
What is DaaS?
Data as a Service (DaaS) is a cloud-based model that delivers data to users on demand, similar to how Software as a Service (SaaS) provides software applications. DaaS abstracts the complexity of data management, allowing businesses to access and utilize data without the need to invest in extensive infrastructure or specialized IT staff. This service model leverages cloud deployments to offer scalable, flexible, and cost-effective data solutions, enabling the entire organization to focus on deriving insights rather than managing data integration, data storage, data processing and data analytics themselves.
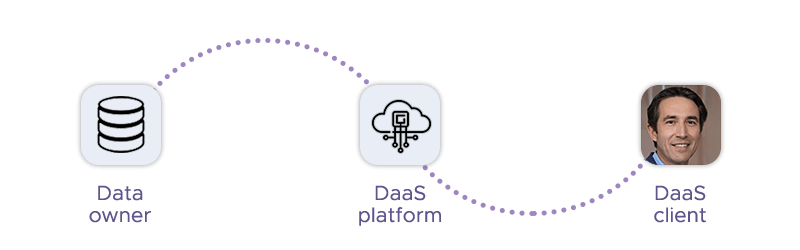
Data as a service platforms aggregate and store data from multiple sources, including internal databases, third-party providers, and web scraping, to provide a set of unifying data. Optionally, they can also process data, clean it, and normalize it to ensure high quality and consistency. Users can later analyze data through various means, such as APIs, dashboards, or data feeds, tailored to their specific needs. The key benefits of DaaS include cost savings, as organizations only pay for the data they use, and the ability to scale resources according to demand. Additionally, DaaS ensures that data is readily available, up-to-date, and accessible in real-time, which is crucial for timely and more agile decision-making.
How DaaS works
A data as a service pipeline involves several stages through which data is collected, processed, and delivered in a usable format:
1. Gather data: Main data sources are typically divided into internal (data generated within the organization’s virtual data layer, such as transactional data, CRM systems, and operational databases) and external (data from outside the organization, such as third-party APIs, public datasets, social media, and web scraping.)
2. Ingest data/consume data: This can be done via batch processing (collecting data at scheduled intervals) or stream processing (continuously collecting data in real-time).
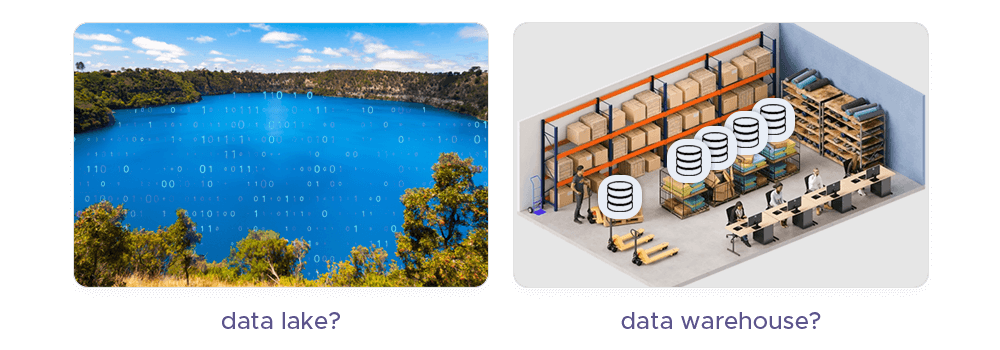
3. Store data: Some options include data lakes (centralized repositories that store raw data in its native format, such as Hadoop HDFS, Amazon S3) and data warehouses (structured data storage optimized for query and analysis. For example, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery). Then, you move data to the next step.
4. Process data: This involves multiple steps: clean data (remove duplicates, handle missing values, correct errors), transform data (normalize, aggregate, and integrate data from different sources), and enrich data (add value by integrating additional data sources or apply algorithms to extract business insights).
5. Perform data analytics: Namely, descriptive (summarize historical data to understand what has happened), predictive (use statistical models and AI/ML algorithms to forecast future trends), or prescriptive (recommend actions based on predictive insights).
6. Deliver data: Some methods include API management (expose data endpoints for real-time access and integration, such as RESTful APIs, GraphQL), data feeds (automated delivery of data files to subscribers at regular intervals), and dashboards (visualize data insights for decision-makers).
7. Safeguard data: Best security practices include data quality management (ensure accuracy, completeness, and reliability of data), access control (implement role-based access and authentication mechanisms), and compliance (adhere to regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA).
DaaS benefits
Just like its counterparts, the data as a service model offers several important benefits. Let’s take a closer look at them – and try to understand if certain DaaS challenges can offset them:
1. Cost savings
One of the primary benefits of data as a service is the cost efficiency it brings to organizations. Traditional data infrastructure requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and human resources to set up and maintain data systems. With data as a service, companies can avoid these capital expenditures. Instead, they only pay for resources they actually use, such as data storage and processing resources. This business model can reduce costs significantly, ensuring that organizations are not burdened by underutilized resources. This flexibility is particularly advantageous for startups and small businesses, which can now access enterprise data services with lower costs.
Additionally, DaaS platforms offer inherent scalability, allowing businesses to adjust their collected data infrastructure in response to changing needs. As a company grows, the volume of data it needs to handle typically increases. DaaS providers offer seamless scalability, enabling businesses to scale up and down when it comes to storage and processing capabilities without the need for additional hardware or significant reconfiguration. Thanks to this flexibility, companies can quickly adapt to market demands and data requirements without the risk of over-provisioning or facing bottlenecks. Conversely, if data needs decrease, organizations can scale down their usage, ensuring they are only paying for what they need at any given time.
2. Reliable access to real-time data
This enables businesses to make timely and informed decisions. When they access real-time data, companies can monitor their operations continuously, respond quickly to emerging trends, and address issues as they arise – anytime and anywhere. This immediacy is crucial for industries like finance, e-commerce, and logistics, where conditions can change rapidly, and quick responses can prevent losses and seize opportunities.
3. Improved application performance

Data as a service enhances application performance by providing optimized and scalable data infrastructure that can handle large volumes of data efficiently. Applications can retrieve and process data faster because a DaaS provider uses advanced technologies and architectures designed for high performance. This leads to quicker response times and a smoother user experience, which is critical for applications where speed and reliability are essential, such as in customer-facing platforms and real-time analytics tools.
Furthermore, DaaS providers often offer geographically distributed data centers, ensuring that data is delivered from the nearest location to the user. This reduces latency and improves access speeds, enabling applications to perform better regardless of the user's location. Improved performance not only enhances user satisfaction but also supports the development of more sophisticated and data-intensive applications, driving innovation and growth.
4. Automated oversight
Automated oversight is another key benefit of DaaS, as it incorporates built-in monitoring, troubleshooting, and data management tools that ensure data integrity, security, and compliance. These automated systems continuously monitor data flows and usage patterns, identifying and addressing potential issues before they become critical. This reduces the risk of data breaches, downtime, and compliance violations, providing peace of mind and allowing businesses to focus on their core activities.
Additionally, automated oversight simplifies the management of complex data environments. It includes automated backups, updates, and patches, ensuring that the data infrastructure is always up-to-date and protected against vulnerabilities. This automation minimizes the need for manual intervention, reduces the potential for human error, and can help to cut costs.
5. Monetization possibilities
DaaS opens up new monetization opportunities by enabling businesses to leverage their data as a valuable asset. Companies can generate revenue and utilize cost savings by offering their data to partners through APIs or data marketplaces. This data can be useful to various industries, including marketing, research, and finance, which can use it for advanced analytics, insights, operational improvements, and decision-making. By monetizing data, organizations can turn their existing data resources into a significant source of income.
Additionally, data as a service facilitates the development of new products and personalized services that are data-centric and focus on customer satisfaction. Businesses can build analytics tools, dashboards, and other data-driven solutions that can be sold or licensed to other companies. These offerings not only generate revenue but also enhance the company’s value proposition by positioning it as a provider of innovative data solutions.
6. Improved end-user experiences
Data as a service significantly enhances the end-user experience by ensuring that data-driven applications are responsive, reliable, and always available. Users benefit from faster load times and smoother interactions because the underlying data infrastructure is optimized for performance. This improvement is particularly important for applications where seamless user interactions are critical, such as in e-commerce, gaming, and mobile apps. A better user experience leads to higher user satisfaction and retention, which are essential for business success.
Moreover, DaaS allows for personalized and real-time interactions by providing access to the most current data for better analysis. Applications can deliver tailored content, recommendations, and services based on the latest user behavior and preferences. This level of personalization not only enhances the user experience but also helps to make better informed decisions.
DaaS challenges

However, there is a reason why some businesses may be skeptical about adopting this model. Let’s dig deeper into data as a service’s potential downsides:
1. Security
Data security is a significant challenge in DaaS as it involves handling sensitive and potentially valuable information across various platforms and networks. Protecting this data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber-attacks requires robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, firewalls, and continuous monitoring. The reliance on third-party providers introduces additional risks, as businesses must trust these providers to implement and maintain stringent security protocols.
2. Privacy
Data privacy concerns in DaaS stem from the need to comply with various privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA. These regulations require stringent controls over how personal data is collected, stored, processed, and shared. Ensuring compliance involves implementing privacy policies, obtaining user consent, and maintaining transparency in data practices. Additionally, the cross-border nature of many existing services can complicate compliance, as different geographic regions have varying data privacy laws. Businesses must carefully navigate these regulations to avoid legal repercussions and maintain user trust.
3. Compatibility
Compatibility is a challenge as data as a service involves integrating data from diverse sources and systems, each with its own formats, standards, and protocols. Ensuring seamless interoperability between these systems can be complex and time-consuming. Businesses need to standardize data formats and establish robust integration frameworks to facilitate smooth data flow and utilization. Additionally, legacy systems may not be easily compatible with modern DaaS solutions, requiring further investments in updates or middleware to bridge the gaps and ensure efficient data operations.
4. Data governance
Effective data governance is crucial in DaaS to ensure data quality, consistency, and compliance. Establishing clear policies and procedures for a data management strategy, including data ownership, stewardship, and accountability, can be challenging. To achieve this, frameworks for monitoring data usage, maintaining data lineage, and ensuring data accuracy must be successfully implemented. This requires collaboration across different departments and alignment with regulatory requirements. Without proper governance, businesses risk data inconsistencies, errors, and compliance issues that can undermine the value and reliability of their data assets.
5. Implementation
A data as a service implementation strategy can be complex, involving significant changes to existing IT infrastructure and processes. Businesses need to assess their current data systems, identify gaps, and develop a comprehensive migration strategy. This often requires skilled personnel and potentially new technology investments, which can be costly and time-consuming. Additionally, managing the data democratization while ensuring minimal disruption to ongoing operations is critical. Effective planning, stakeholder buy-in, and phased implementation can help mitigate these challenges and ensure a smooth transition to a DaaS environment.
Major DaaS use cases
The DaaS model is used in numerous industries — let's explore why healthcare, finance, e-commerce, manufacturing, and marketing companies prefer it over the alternatives:
Healthcare
In healthcare, data as a service is used to integrate and analyze vast amounts of patient data from various sources such as electronic health records (EHRs), wearable devices, and medical imaging. By providing real-time access to all the data, healthcare providers can enhance patient care through better diagnostics, personalized treatment plans, and predictive analytics for disease prevention. DaaS also facilitates data sharing and collaboration among different healthcare institutions and researchers, enabling more effective clinical trials and advancing medical research.
Finance
In the finance sector, data as a service is utilized to manage and analyze large data sets from transactions, market feeds, and customer interactions. Financial institutions use DaaS to gain insights into market trends, assess risks, and enhance fraud detection capabilities. Real-time business data access allows for more accurate trading strategies and financial forecasting. Additionally, DaaS supports regulatory compliance by providing a robust framework for managing and reporting financial data in accordance with various regulations.
E-commerce

E-commerce businesses leverage DaaS to enhance customer experience and optimize operations. By analyzing data from customer interactions, purchase histories, and website behavior, companies can provide personalized product recommendations, improve inventory management, and tailor marketing campaigns. Real-time data access helps e-commerce platforms quickly respond to market changes, optimize business strategies, and manage a supply chain more efficiently, ensuring a seamless shopping experience for customers.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, data as a service is used to collect and analyze data from production lines, machinery, and supply chains. This data-driven approach helps optimize manufacturing processes, improve product quality, and reduce downtime through predictive maintenance. By integrating data from various sources, manufacturers can gain real-time visibility into their operations, allowing for better decision-making and increased efficiency. DaaS also supports the implementation of Industry 4.0 initiatives, such as smart factories and IoT-driven automation.
Marketing and Advertising
Marketing and advertising agencies use data as a service to gather and analyze data from multiple channels, including social media, websites, and customer databases. This data is used to create targeted marketing campaigns, measure campaign effectiveness, and understand consumer behavior. Real-time analytics enable marketers to adjust strategies on the fly and maximize ROI. DaaS also allows for the integration of third-party data sources, providing a more comprehensive view of market trends and consumer preferences, which enhances the precision and impact of marketing efforts.
How Web Scraping Contributes to DaaS
Web scraping plays a crucial role in data as a service by enabling the automated extraction of vast amounts of data from websites and online sources. This process involves using software tools or scripts to collect information from web pages, which can then be structured, stored, and made available through DaaS platforms. Here are some ways web scraping contributes to DaaS:
Automated data gathering: Web scraping allows DaaS providers to continuously collect data from various online sources without manual intervention. This includes information from e-commerce sites, social media platforms, news websites, and more data. By automating data collection, web scraping ensures that the DaaS platform has a steady and up-to-date stream of information, which is essential for delivering real-time data services.
Expanding data sources: Through web scraping, data as a service providers can access a broader range of data sources, including those not traditionally available through APIs or public datasets. This capability expands the diversity and richness of the data available in the DaaS offering, enhancing its value for users who require comprehensive and varied data for analysis and data-driven decision-making.
Real-time updates: Web scraping tools can be configured to regularly check for and extract updated information from websites. This ensures that the data provided through the DaaS platform is always current, which is particularly important for applications that rely on real-time data, such as financial trading, market analysis, and news aggregation.
Best Practices for Successful DaaS Adoption
Building a data as a service pipeline is a complicated task – but you can make it easier with these business practices:
Establishing Clear Data Governance
To successfully adopt DaaS, organizations must establish clear data governance policies that define how data is managed, accessed, and used. This involves setting up a framework that outlines data ownership, data stewardship, and the responsibilities of various stakeholders. Clear roles and responsibilities ensure accountability and help maintain data integrity and security.
Data governance also includes ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and implementing robust security measures. Organizations must develop policies that address data privacy, protection, and compliance with laws such as GDPR and CCPA. Regular audits and assessments should be conducted to ensure these policies are being followed, mitigating risks associated with data breaches and non-compliance.
Ensuring Data Quality and Accuracy
High-quality and accurate data is crucial for effective data as a service adoption. Organizations should implement data validation processes to check for errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates. This can involve automated tools that perform data cleansing and manual checks for critical data points. Ensuring data quality from the outset prevents issues downstream in data processing and analysis.
Organizations should also establish mechanisms for continuous monitoring and improvement of data quality. This includes regular reviews and updates to data sources and validation rules. Feedback loops from data users can help identify recurring issues and areas for improvement, ensuring that the data remains accurate and reliable over time.
Integration with Existing Systems
For a successful DaaS adoption, it’s essential to ensure seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure and business applications. This requires leveraging APIs, middleware, and data connectors that facilitate the smooth flow of data between the DaaS platform and existing systems. Ensuring compatibility and interoperability minimizes disruptions and enhances the value derived from the data as a service solution.
Special attention should be given to integrating legacy systems, which may require additional tools or custom solutions to interface with modern DaaS platforms. Organizations should assess their current systems and plan integration strategies that minimize downtime and ensure data consistency across all platforms.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Continuous monitoring and evaluation are critical to maintaining the effectiveness of a DaaS implementation. Organizations should track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to data usage, system performance, and user satisfaction. This helps identify any issues early and allows for timely interventions to address them.
Regularly collecting feedback from data users and stakeholders is essential for the ongoing success of DaaS. This feedback can be used to make iterative improvements to any data service, ensuring they meet evolving business needs. Continuous evaluation also involves updating data governance policies, integration processes, and data quality measures to adapt to new challenges and opportunities.