Dive into the world of IP hopping with our comprehensive article, designed to enhance your understanding of online privacy and content accessibility. Learn the ins and outs of evading digital tracking and regional restrictions, while exploring the ethical use of web scraping tools.
How IP Hopping Works
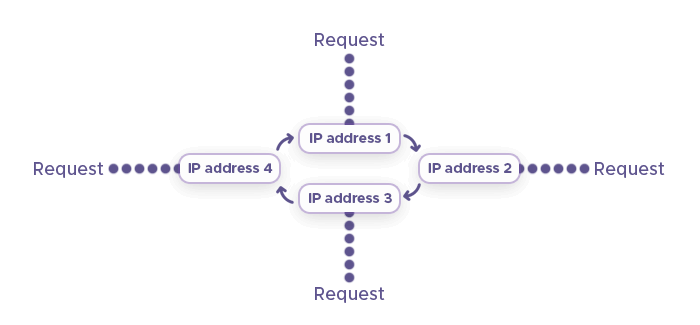
IP hopping is a technique used to switch between different IP addresses over a period of time. This practice is essential for various online activities, offering benefits in internet security, data privacy, and access management.
IP hopping involves using one IP address for a certain duration before transitioning to another. This method helps users conceal their actual IP address, thereby avoiding potential flags or bans from websites they visit. It's particularly useful in automation and data intelligence tasks, where multiple connections are sent out. Here are its major practical applications:
- Fast Anonymity: Used by professionals for secure data exchange between known parties, changing IP addresses in a predetermined pattern.
- Privacy and Security: Individuals employ IP hopping to maintain anonymity and protect their online identity.
- Data Scraping and Shopping Bots: It's crucial for tasks like data scraping or using bots to purchase limited-edition items, as it helps circumvent IP-based restrictions and bans.
While IP hopping offers many advantages, it also comes with challenges. Websites with robust security measures may detect and ban users for unusual IP changes. To avoid this, it's recommended to use proxy IP addresses from the same country or region and to manage cookies effectively.
Dynamic IP vs. Static IP
Dynamic IPs are particularly suitable for IP hopping because of their inherent flexibility and the way they are assigned. Since dynamic addresses are allocated automatically and can change with each new connection.

Static IP Addresses:
- Permanence: A static IP address is a permanent address that doesn't change.
- Assignment: It is manually assigned to a device and remains constant until changed manually.
- Use Cases: Ideal for servers or other devices that need to maintain the same IP address for a long time.
- Stability: More stable as it does not change over time.
- Security: Can be less secure as the constant address can be more susceptible to targeted attacks.
- Cost: Usually more expensive to maintain due to their fixed nature.
Dynamic IP Addresses:
- Permanence: A dynamic IP address can change every time a device connects to the network.
- Assignment: Assigned automatically by a DHCP server from various IP pools.
- Use Cases: Suitable for consumer devices that do not require an IP from the same user.
- Flexibility: More adaptable, perfect for environments where devices frequently join and leave the proxy network.
- Security: Generally more secure as the changing IP address makes it harder for attackers to target the device.
- Cost: Less expensive as they are easier to manage and do not require manual configuration.
Proxy Servers and Their Role
Proxy servers play a crucial role in the process of IP hopping by acting as intermediaries between the user's device and the internet. Here's how they facilitate it:
- Anonymity: Proxy servers provide anonymity by masking the user's real IP address with their own. This is essential for IP hopping, where the goal is to change the IP address frequently to avoid flags.
- Request Forwarding: They receive connection requests from a user's device and forward them to the internet, making it appear as though the request is coming from the proxy server's IP address.
- Data Filtering: Proxies can filter and modify data, which can be used to manage cookies and other identifying information that could compromise the IP hopping process.
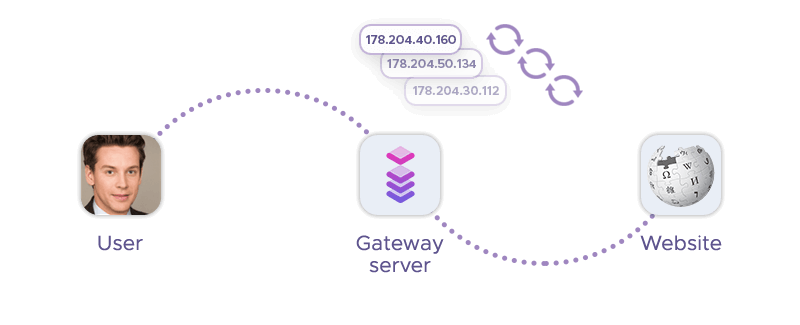
Furthermore, proxy servers have access to an IP pool, often from various locations and ISPs, which can be rotated to implement IP hopping. Many of them offer automated IP rotation, which can change the user's IP address at set intervals or with each new connection. By using proxies from specific countries or regions, users can comply with geo-restrictions while still changing their IP addresses.

VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) for IP Hopping

VPNs are another way of performing the IP hopping process – they add an extra layer of encryption and data security. Here's how they contribute to it:
- Enhanced Encryption: VPNs encrypt data traffic not just once, but multiple times if configured for multi-hop or double VPN connections. This means that your data is encrypted at each hop, making it increasingly difficult for anyone to track or decipher your online activities.
- Multiple Server Hops: With a multi-hop VPN, your internet traffic is routed through two or more VPN servers before reaching its final destination. Each server hop changes your IP address and adds a new layer of encryption, significantly boosting your anonymity and making it harder for malicious actors to follow your digital trail.
- Increased Anonymity: Each VPN server in the chain only knows the IP address of the previous server, not the original source of the traffic. This means that even if one server were compromised, it would not reveal your actual IP address or location, thus preserving your privacy.

Tor Network and Anonymity
The Tor network, also known as The Onion Router, is designed to provide anonymity and privacy online by routing internet traffic through a global network of volunteer-run servers. On Tor, IP bouncing lets users browse more privately via:
- Entry Node: Your connection enters the Tor network through an entry node, but this node does not know where your data will exit the network.
- Relays: The data passes through several relays, each one decrypting a layer of encryption, but no single relay knows both the source and the final destination of the data.
- Exit Node: The exit node removes the final layer of encryption and sends the data to the destination. The exit node appears as the source of the traffic to the destination, not your actual IP address.
And here’s how Tor can improve your anonymity and privacy:
- Layered Encryption: Tor uses layered encryption, which means data is encrypted multiple times as it passes through multiple backconnect nodes, or relays, in the Tor network.
- Randomized Path: Each internet request goes through a series of relays, and the path is randomized, making it extremely difficult to trace the activity back to the user.
- No Direct Communication: Your device communicates with the final destination indirectly, ensuring that your IP address is not exposed to the destination website.
- Bridges: Tor also uses bridges, which are non-public relays, to help users connect to the network when access is blocked or censored.
- No Tracking: Since no single point in the Tor network has both the origin and destination information, tracking users' activities is incredibly difficult.
Why Bounce Your IP Address?
There are several major reasons to bounce IP addresses frequently:
Privacy Concerns
Users may choose to get new IP addresses for privacy reasons to prevent their online activities from being easily tracked and monitored. Here are some key reasons why this is done:
- Anonymity: IP bouncing lets users browse the internet without revealing their actual IP address, which can be linked to their personal identity or location.
- Avoid Tracking: Advertisers, websites, and cybercriminals can use IP addresses to track users' online behavior, build profiles, and deliver targeted ads. Bouncing an IP helps avoid this type of tracking.
- Access Restrictions: Some content on the internet may be restricted based on geographic location. Bouncing an IP can circumvent these restrictions, allowing access to a broader range of content.
- Security: Public IP addresses can be tracked to an individual's internet service provider, potentially exposing them to monitoring by various entities. Using methods to bounce or hide an IP address can enhance security and reduce the risk of cyber threats.
Web Scraping Benefits
IP hopping during web scraping is a technique used to avoid detection and blocking by websites. Here's why it's done:
- Avoiding IP Bans: Websites often disallow large numbers of packets from a single IP address to prevent abuse. By changing IP addresses frequently, web scrapers can evade these limits and continue scraping data.
- Maintaining Anonymity: Using different IP addresses helps conceal the identity of the scraper, making it more difficult for websites to track and block them.
- Data Quality: For comprehensive data intelligence, scrapers may need to access websites from various locations. IP hopping allows for location-specific scraping, ensuring a diverse and accurate dataset.
- Efficiency: Large-scale web scraping operations involve sending thousands of requests. Using multiple proxies through IP hopping ensures that these operations can run smoothly without overloading a single proxy.
- Legal Compliance: In some cases, IP hopping can be used to comply with legal restrictions on data access from specific regions or to respect rate limits set by websites.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
While IP hopping has legitimate uses, such as maintaining privacy and security online, there are several legal and ethical considerations to keep in mind:
- Infringement Risks: Frequent changes in IP addresses can raise suspicions of infringement or other illegal activities, leading to potential legal consequences.
- Security Risks: IP hopping can be used by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to different network segments, posing significant security risks.
- Detection and Bans: Websites may detect unusual IP changes and impose bans, which can affect legitimate users who are not engaging in any wrongful activity.
Problems With Bouncing Your IP Address
When it comes to IP hopping, frequently changing IP addresses can indeed lead to IP blocks, especially if the behavior is detected as unusual or suspicious by many online services. This is because many systems have automated security measures to detect and prevent potential abuse, such as scraping or unauthorized access, and rapidly changing IP addresses can trigger these defenses.
Using IP addresses from different countries may increase the likelihood of being flagged by anti-scraping systems, as it aligns more closely with typical scraper behavior. Furthermore, sophisticated systems may use additional parameters to detect scraping activities.
Clearing cookies can also be a part of avoiding detection, but it's not guaranteed to work on its own. Anti-scraping systems may employ a variety of techniques to identify and block scraping bots, including analyzing behavior patterns, observing unusual changes in request rates, and other fingerprinting methods.
How To Bounce Your IP Address With a Proxy Server
A typical proxy server may have a pool of proxy IP addresses that you can use to rotate IPs. Let’s analyze two major proxy types and how they compare against each other:
ISP proxies
ISP proxies, also known as static residential proxies, are a hybrid between data center proxies and residential proxies. ISP proxies are hosted in data centers but are registered under the autonomous system numbers (ASNs) of an Internet Service Provider (ISP). This gives them the authority of residential proxies, which are less likely to be blocked by websites looking for proxy traffic. At the same time, they maintain the speed and reliability of data center proxies because they are hosted on high-bandwidth servers.
By using ISP autonomous system numbers, ISP proxies gain more authority and trust from websites, as they appear to be coming from a legitimate ISP rather than a data center. This makes it less likely for them to be blocked, while still providing the high speed associated with data center proxies.
To avoid detection and blocking, it's also important for these proxies to mimic human-like traffic patterns, use appropriate session management, and rotate IP addresses smartly. This helps in maintaining the efficacy of the proxies for various online operations, such as web scraping or managing multiple online accounts.
Rotating proxies
Rotating residential proxies are considered the gold standard for IP address rotation: They offer a high level of authority and are effective at circumventing anti-scraping technologies. Here's why they are so valuable:
- Authentic IP Addresses: They use real IP addresses assigned to real users, making them less likely to be flagged as proxies by websites.
- Rotation: These proxies change the IP address after every request or at regular intervals, which helps to mimic the behavior of multiple users and avoid detection.
- Overcoming Geo-Restrictions: They allow users to appear as if they are located in different geographical locations, which is useful for bypassing regional content restrictions.
- Avoiding Blocks and Bans: The constant rotation makes it difficult for websites to track and block the user's IP address, thus reducing the risk of being blacklisted.
- Data Scraping: For tasks like web scraping, rotating residential proxies are particularly useful because they can make a large volume of requests without triggering anti-bot measures.
Setting Up Proxies for IP Hopping with Infatica
Setting up proxies with Infatica involves a few steps. Here's a general guide on how to bounce IP addresses:
- Sign Up for Infatica: Create an account with Infatica and choose the type of proxies you need for your project, such as residential, mobile, or data center proxies.
- Access Proxy Dashboard: Once you have an account, log in to the Infatica dashboard to access your proxy list and manage your settings.
- Generate Proxy List: In the dashboard, you can generate a list of proxies by selecting your desired locations, types, and other settings. This list will contain the IP addresses and ports that you will use for IP hopping.
- Configure Proxy Settings: Use the generated proxy list to configure the proxy settings in your web scraping tool or software. This usually involves entering the IP addresses, ports, and any required authentication details.
- Implement IP Rotation: To hop between different IP addresses, you’ll need to set up a rotation mechanism. This can be done manually or automatically, depending on your tool’s capabilities. Some tools allow you to specify a rotation interval or trigger IP changes based on certain conditions.
- Test Your Proxies: Before starting your web scraping tasks, it’s important to test the proxies to ensure they are working correctly and that your IP rotation setup is functioning as expected.
- Start Scraping: With everything set up, you can begin your web scraping activities. The proxies will rotate according to your configuration, helping you avoid detection and IP bans.
Conclusion
Our article has equipped you with the essential knowledge of IP hopping, emphasizing its role in maintaining online anonymity and accessing global content. Armed with these insights, even inexperienced IP bouncers can confidently apply ethical web scraping practices to their digital endeavors. Happy scraping!